About cord blood and its importance-
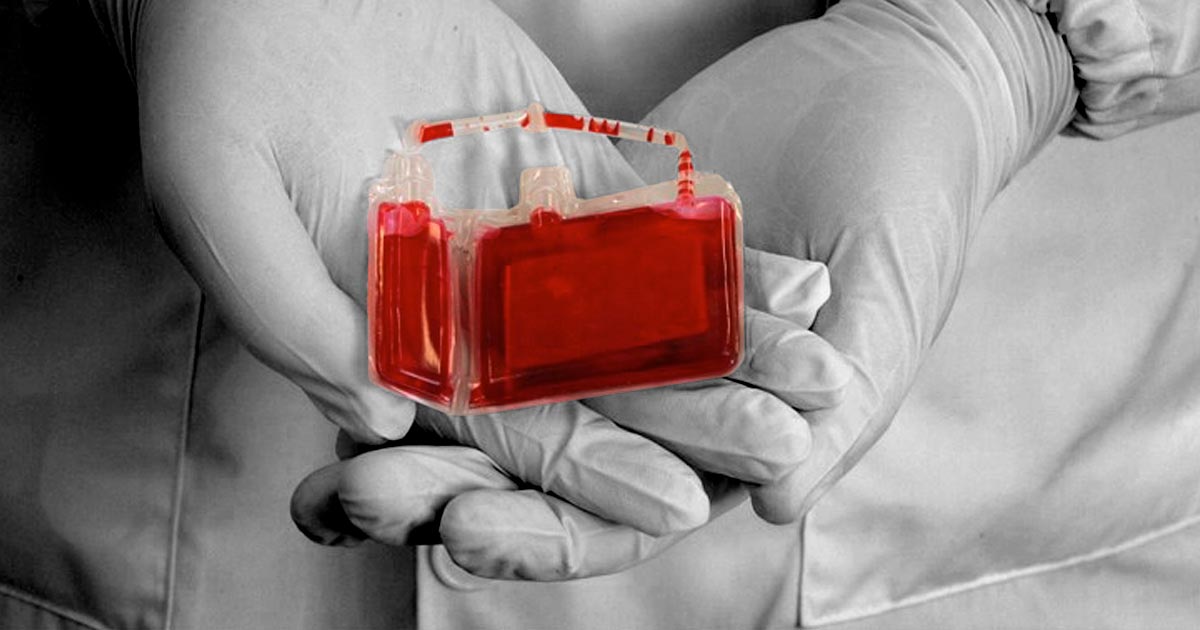
Cord blood, also known as umbilical blood, is the blood present in both the umbilical cord and placenta after birth. This cord blood contains stem cells and other immune system cells in abundance. Cord blood banking involves the collection of cord blood and the extraction and cryogenic freezing of stem cells and other immune system cells extracted from it for future medical use.
Cord blood banking is often used as a generic term for all the cells stored. Some parents may be surprised to discover that cord blood kept in storage contains very little of what we call “blood”. In fact, red blood cells (RBCs) can be harmful to cord blood treatments. One of the main goals of cord blood processing is to reduce the amount of red blood cells in any cord blood collection.
Cord blood banking is also known as stem cell banking in Europe and elsewhere. This may be because cord blood banking is more about collecting blood-forming stem cells and not actual blood cells.
Before the 1990s, the umbilical cord and its blood were considered medical trash. Parents today store or bank their baby’s umbilical blood, as the stem cells found in it can be used to treat life-threatening or debilitating conditions.
Expectant parents have the advantage of being able to collect cord blood at their baby’s birth using the umbilical cord. This can be done without any harm to either the baby or the mother.
There are numerous reasons to bank cord blood stem cells from your baby. These are-
- Cells extracted from cord blood are an exact match for the recipient in case of an autologous transplant. Autologous transplants are those where the donor and the recipient are the same person.
The cord blood you store for your baby is a medical resource that can be used in the future. It does not require strict matching, unlike conventional bone marrow stem cells transplants. Since around 70% of transplant patients are not able to find a match within their family, cord blood banked could prove lifesaving.
- In case of an emergency or some critical health condition, you will have stored haematopoietic stem cells readily available for treatment. If your child is in a critical situation and stem cells are needed for a transplant, then searching for it could be a lot of hassle. And that is why it makes sense to have the cord blood of your baby stored so that it can be used in the future for such criticalities. This saves you both time and money.
- Graft vs. Host Disease (GvHD) is a serious condition often seen after autologous transplants. Graft vs. Host Disease is a condition where transplanted tissue causes damage to the patient’s own tissues. This is most common in transplants where the recipient and donor are not the same. Cord blood banking can eliminate this risk.
- Here is the best benefit of cord blood banking the collection is painless and risk-free for both the mother and baby. Cord blood collection can be done without difficulties— it is a simple task. The process is not intended to interfere with the birthing process and can be performed on natural as well as c-section births.
- The stem cells of umbilical cord blood are younger than those collected from elsewhere. That means umbilical cord stem cells can grow healthy stem cells faster than other types of stem cells, such as those from bone marrow or peripheral blood or from other sources.
- One in 217 people have the chance to use stem cells as a treatment for their condition in their lifetime. That is a huge probability, even though it might not seem so. These stem cells are found in your baby’s cord blood. Cord blood stem cells have been used by doctors to treat over lakhs of patients with diseases like blood disorders and certain cancers. Cord blood stem cells have also been used in clinical trials.
- More people receive help from stem cells sourced from cord blood than from bone marrow. The reason is that the recipient of the transplant does not need to match the cord blood exactly, but the same isn’t true for stem cells extracted from other sources. And that is why the chances of stem cells being rejected by the body from cord blood are lower than those from bone marrow.
- During cancer treatment, cord blood stem cells can support the immune system. This is not possible with stem cells taken from bone marrow.
- Cord blood collection is not just easier and less painful; it is also less risky than bone marrow collection. Both the new-born and the mother-to-be are free from risks when cord blood collection is done.
Cord blood banks can store and freeze cord blood, so it is always available for use. It is completely free to donate cord blood to a public bank. Also, the donation of cord blood can save lives.0